the future of robots
Electronics & Technology
Robots need better batteries. Mobile robots can dance around a stage, run, perform acrobatics, lift heavy objects and do some very advanced functions today. But if you watched them carefully for an hour or two, you would see the robots grind to a halt. Robots eventually exhaust the energy that they carry and need a recharge.
whitepaper
A proposal to improve Robots - Photovoltaic (PV) development
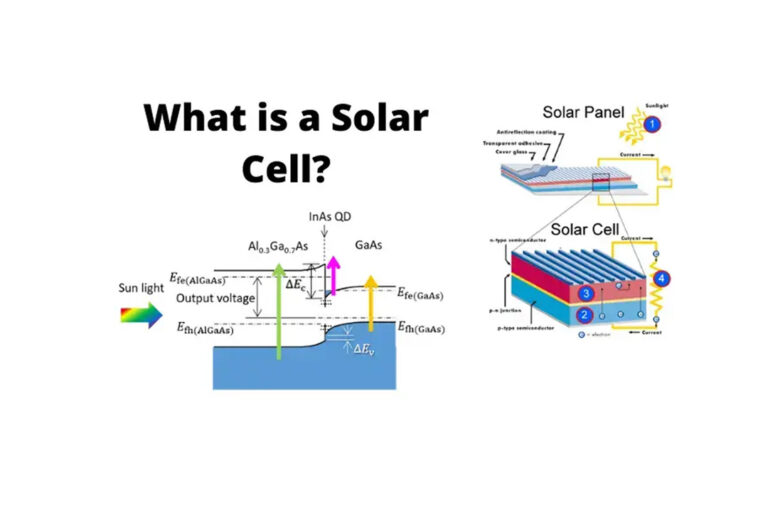
Photovoltaic (PV) development is the process of researching, designing, and manufacturing solar cells and panels that convert sunlight into electricity. Photovoltaic cells are made from semiconducting materials, typically silicon, that absorb sunlight and release electrons, creating an electric current.
Here’s a breakdown of the key areas of photovoltaic development for solar power:
1. Material Science:
- Developing new and more efficient materials: Researchers are constantly looking for ways to improve the efficiency of solar cells. This involves developing new materials that can absorb a wider range of sunlight or convert sunlight into electricity more efficiently.Silicon solar cell
- Reducing material costs: Silicon is the most common material used in solar cells, but it can be expensive. Researchers are developing ways to reduce the cost of silicon or to use less expensive alternative materials.
2. Cell Design and Manufacturing:
- Improving cell efficiency: Cell design plays a crucial role in efficiency. Researchers are developing new cell architectures and structures to capture more sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Lowering manufacturing costs: Manufacturing processes for solar cells are constantly being improved to reduce costs and increase production capacity.
3. Solar Panel Design and Integration:
- Enhancing durability and weather resistance: Solar panels need to be able to withstand harsh weather conditions, such as extreme temperatures, hail, and wind. Researchers are developing new materials and coatings to improve the durability of solar panels.
- Aesthetics and Building Integration: Solar panels are becoming more aesthetically pleasing and easier to integrate into buildings. This is making solar power a more attractive option for homeowners and businesses.
4. System Integration and Balance of System (BOS) Components:
- Optimizing inverters and other BOS components: Inverters convert the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used by homes and businesses. Researchers are developing new inverter technologies that are more efficient and reliable.
- Smart grid integration: As more solar power is added to the grid, it is important to be able to integrate it effectively. Researchers are developing new technologies that can help manage the variability of solar power and ensure that the grid remains stable.
the future of robots
Cell Design and Manufacturing:
The Future of Photovoltaic Development
- Improving cell efficiency: Cell design plays a crucial role in efficiency. Researchers are developing new cell architectures and structures to capture more sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Lowering manufacturing costs: Manufacturing processes for solar cells are constantly being improved to reduce costs and increase production capacity.
Photovoltaic development is a rapidly evolving field. New technologies are constantly being developed that are making solar power more efficient, affordable, and reliable. As a result, solar power is becoming an increasingly cost-competitive source of electricity.
Here are some of the trends that are likely to shape the future of photovoltaic development:
- Perovskite solar cells: Perovskite solar cells are a new type of solar cell that has the potential to be much more efficient than traditional silicon solar cells. Researchers are working on improving the stability and durability of perovskite solar cells so that they can be commercialized.
- Tandem solar cells: Tandem solar cells are made from two or more layers of different semiconducting materials. This allows them to absorb a wider range of sunlight than traditional solar cells, which can improve their efficiency.
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV): BIPV is the integration of solar panels into the building envelope. This can be a very cost-effective way to generate solar power, as the solar panels can also serve as roofing or cladding materials.
By continuing to invest in photovoltaic development, we can make solar power a more affordable and accessible source of clean energy for everyone.
- Material Selection and Purification
- Wafer Formation
- Cell Junction Formation
- Texturing and Etching
- Metallization and Interconnection
- Encapsulation and Testing
Exciting Solutions for Robots
Imagine Robots can charge themselves with photovoltaic cells
Photovoltaic cells (also known as solar cells) have the potential to power robots but with some limitations. Here’s a breakdown of the feasibility:
Feasibility:
Suitable for Low-Power Robots: Photovoltaic cells are a viable option for powering small, low-power robots. These robots typically have lower energy demands and operate in environments with consistent sunlight exposure. Examples include:
- Lawn mowing robots
- Small delivery robots
- Security robots for patrolling purposes
Integration Considerations: The robot’s design needs to incorporate solar panels efficiently to capture enough sunlight for its power needs.
Solar Energy Availability: Robots powered by solar cells rely on sunlight for charging. This can be a limitation in areas with limited sunlight hours or during cloudy weather.
Limitations:
- Power Output: Current solar cell technology may not generate enough power for robots with high energy demands, such as industrial robots or robots performing complex tasks. These robots might require frequent recharging or alternative power sources.
- Battery Backup: Even for low-power robots, a backup battery system is recommended to account for periods of low sunlight or unexpected power demands.
Current Applications:
Solar-powered robots are making an entrance in various fields:
- Environmental Monitoring: Robots equipped with solar panels can be deployed for long-term environmental monitoring tasks in remote locations.
- Agricultural Applications: Solar-powered robots are being developed for tasks like weed removal or crop monitoring in fields where access to power outlets might be limited.
Future Potential:
- Advancements in Solar Cell Technology: As solar cell efficiency improves and the cost of solar panels continues to decrease, solar power could become a more viable option for a wider range of robots.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Developments in battery storage technology can help robots utilize solar energy more effectively by storing excess energy generated during sunlight hours.
Overall, photovoltaic cells can be a sustainable and efficient way to power some robots, particularly low-power robots operating in sunny environments. However, current limitations in power output and energy storage necessitate careful consideration for broader applications.
Photovoltaic Cells can be planted on Robots Heads, Arms and Shoulders for direct sunlight to recharge.

Company Proposal for a ground-breaking Opportunity
Our CEO is very passionate about engineering, and there is an opportunity to take Robots to the next generation by solving Robots biggest problem. Power, Energy, Battery, Recharge?
SynthoSense is looking for opportunities to Partner and work with Academic Institutes, Businesses or Electronic Engineers to develop the next Generation of PhotoVoltaic Cells which can convert sunlight directly into 1000% more electricity than current cells. The current cells are a huge drawback. We need to develop better Technology.
If we can together pass this milestone we can pave the way for a new Generation of Robots which can Re-Charge themselves and which can operate much more efficiently and much longer without charging themselves.